SNP Calling with RNASeq data
SNP Calling with RNASeq Data
EpiDiverse Bleaching Pairs Analysis
EpiDiverse SNP Analysis for KBay Bleaching Pairs
Mcap Genomic Feature Analysis
Genomic Feature Analysis: M. capitata
Pacuta Genomic Feature Analysis
Genomic Feature Analysis: P. acuta
CpG OE Analysis for DNA Methylation
Historical DNA Methylation Analysis: CpG O/E
Pocillopora acuta v2 Functional Genome Annotation
Pocillopora acuta v2 Functional Genome Annotation
Andromeda Clean-Up
Andromeda Clean Up Fall 2022
M.capitata Genome v3 Functional Annotation
Montipora capitata v3 Functional Genome Annotation
DNA Methylation Analysis Central Working Document
DNA Methylation Sequencing Analysis Central Document
16S-V3V4 Test Run Analysis Pipeline
Analysis Pipeline for 16S V3V4 Test Sequencing Run 1
Holobiont Integration ITS2 Pipeline 2022
Holobiont Integration ITS2 Bioinformatics pipeline - Andromeda version
Statistics - contrast options in models
Statistics: Contrasts and deviation coding
Point Judith Oyster DNA Methylation (MBD-BS)
Point Judith Oyster DNA Methylation
AH Mcap2021 Physiology Processing
AHuffmyer Mcap 2021 physiology processing
16S V3V4 Sample Processing
Sample Processing for 16S V3V4 primers
Point Judith Oyster Gut 16S V6 Analysis
Point Judith Oyster Gut 16S V6 QIIME2 Analysis
E5 Timepoint 1, 2, 3, and 4 Instantaneous Calcification Sample Processing (Samples Collected in 2020)
Processing the E5 January, March, September, and November 2020 Instantaneous Calcification Samples
Point Judith Oyster Gut 16S V4V5 Analysis
Point Judith Oyster Gut 16S V4V5 QIIME2 Analysis
16S Analysis Central Working Document
16S rRNA Sequencing Analysis Central Document
Holobiont Integration 16S Mothur Pipeline
Holobiont Integration 16S V4 Mothur Pipeline
KBay Bleaching Pairs RNASeq Pipeline Analysis
KBay Bleaching Pairs RNASeq Pipeline Analysis
KBay Bleached Pairs 16S Analysis Mothur
KBay Bleached Pairs 16S Sequencing Analysis Pipeline with Mothur
KBay Bleaching Pairs ITS2 Analysis Pipeline
KBay Bleaching Pairs ITS2 Analysis Pipeline
KBay Pairs 16S Analysis Pipeline
KBay Bleached Pairs 16S Sequencing Analysis Pipeline with QIIME2
KBay Bleaching Pairs 16S Processing
KBay Bleaching Pairs 16S Processing
KBay Bleaching Pairs WGBS Analysis Pipeline
KBAY WGBS Methylation Analysis Pipeline
HoloInt WGBS Analysis Pipeline
HoloInt WGBS Methylation Analysis Pipeline
E5 16S Analysis
16S Analysis for Mo’orea E5 project
P. meandrina RNA DNA Extraction
DNA RNA Extraction for Pocillopora meandrina
M.capitata 1312 DNA RNA Extraction
DNA RNA Extraction for Montipora capitata 1312
16s Analysis Pipeline
Holobiont Integration 16S V4 QIIME2 Analysis Pipeline
Cellometer Protocol
Nexcelom Cellometer Vision Putnam Lab Protocol
Cell Counting HoloInt
Symbiont Density Processing
KBay Dec July 2019 WGBS
KBay Bleaching Pairs WGBS Prep: July and December 2019
HoloInt WGBS Sample Processing
Holobiont Integration WGBS Sample Processing
Protein Kit Test
Protein Kit Comparison Test
KBay Dec 4 Physiology
Physiology Processing for Dec and July 2019 time points
KBay Coral Chipping 2021
KBay Coral Chipping 2021
16s Sequencing Processing
16S Sequencing Protocol for the Putnam Lab
Creating a Jupyter Notebook
Creating a Jupyter Notebook
Bioinformatics Data Skills Notes
Bioinformatics Data Skills
Kbay Bleaching 2019 DNA RNA Extractions
DNA RNA Duet Extractions for Kbay Bleaching 2019 Project
WGBS Pico Methyl Seq Test Run
WGBS Pico Methylation Protocol Trials
mtORF Amplification Pocillopora
mtORF Amplification for Pocillopora spp. corals
Physiology Assays Bleaching Fragment Test
’’
Holobiont Integration March Extractions
March DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration Wax Dipping Surface Area
Holobiont Integration Physiology Processing: Wax Dipping Surface Area
Holobiont Integration September DNA RNA Extractions
September DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration October DNA RNA Extractions
October DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration November DNA RNA Extractions
November DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration June DNA RNA Extractions
June DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration July DNA RNA Extractions
July DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration December RNA DNA Extractions
December DNA RNA Extractions
Holobiont Integration August DNA RNA Extractions
August DNA RNA Extractions
ITS2 Sequencing Protocol
Putnam Lab ITS2 Sequencing Protocol
Holobiont Integration Airbrushing
Holobiont Integration Physiology Processing: Airbrushing
Becker DNA RNA Extractions
Danielle Becker Coral Samples Processing January 2020
DNA RNA Extractions
20200123 Test DNA RNA extraction round for Danielle Becker coral samples.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 692-696
20191216 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 685-692
20191210 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 675-684
20191209 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 665-674
20191208 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 653-664
20191206 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 645-652
20191205 M.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 625-644
20191204 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 605-624
20191202 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 595-604
20191125 M.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extrations 575-594
20191121 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
16s, ITS2, 23s PCR Protocol Testing
20191119 R.S., E.S.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
20191113 M.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
20191111 E.S., A.M. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
20191105 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Ash Free Dry Weight Protocol
Putnam Lab Ash-Free Dry Weight Protocol
ImageJ Bleaching Analysis Protocol
Putnam Lab ImageJ Protocols
Total Antioxidant Capacity Protocol
Putnam Lab Total Antioxidant Capacity Protocol
Physiology Protocol Testing
Physiological Parameters Protocol Testing
Chlorophyll-A Protocol
Putnam Lab Chlorophyll-A Concentration Protocol
Total Protein Protocol
Putnam Lab Total Protein Protocol
Holobiont Integration Physiology Pipeline
Holobiont Integration Physiological Analysis Pipeline
Airbrushing Protocol
Putnam Lab Airbrushing Protocol
Qubit, Gel, Tape for re-dos
20191015 E.C.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions 515-518
20191014 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
20191009 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
20191001 E.S. DNA/RNA Extractions from Montipora capitata and Pocillopora acuta adult coral fragments from Holobiont Integration Hawaii 2018 project.
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #475-484
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #465-474
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #457-464
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #417-456
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #395-416
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #375-394
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #363-374
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #351-362
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #343-350
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #333-342
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #323-332
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #303-322
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #283-302
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #267-282
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #255-266
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #227-254
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #179-226
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #155-162; #163-178
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #147-154
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #139-146
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions 119-138
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #119-138
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #91-118
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #83-90
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #73-82
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #53-72
Soft and Hard Homogenization Extractions
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #33-52
Soft and Hard Homogenization
Soft and Hard Homogenization DNA/RNA Extractions #1-32
Testing Soft and Hard Homogenization Round 4
20190716 E. Strand
Gel Electrophoresis Protocol
Putnam Lab Gel Electrophoresis Protocols
Testing Soft and Hard Homogenization Round 3
Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol Testing Round 3
Testing Soft and Hard Homogenization Round 2
Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol Testing Round 2
Testing Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol
Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol Testing Round 1
Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol
Soft and Hard Homogenization Protocol
Major Goal: To extract DNA and RNA from coral fragments and to enrich for host in the first “soft homogenization” fraction and holobiont in the “hard homogenization” fraction. Testing to see if “Soft homogenization” will include DNA and RNA from primarily the host for transcriptomics and DNA methylation analysis. “Hard homogenization” will include the DNA from the symbionts and microbiome for ITS2 and 16s amplification and Holobiont RNA.
Major Results: In the below protocol, the “soft” and “hard” homogenizations did not show a difference quantitatively or qualitatively in symbiont communities. “Mix S” = a mixture of soft homogenization extractions and “Mix H” = a mixture of hard homogenization extractions. There is no clear difference in extraction method.
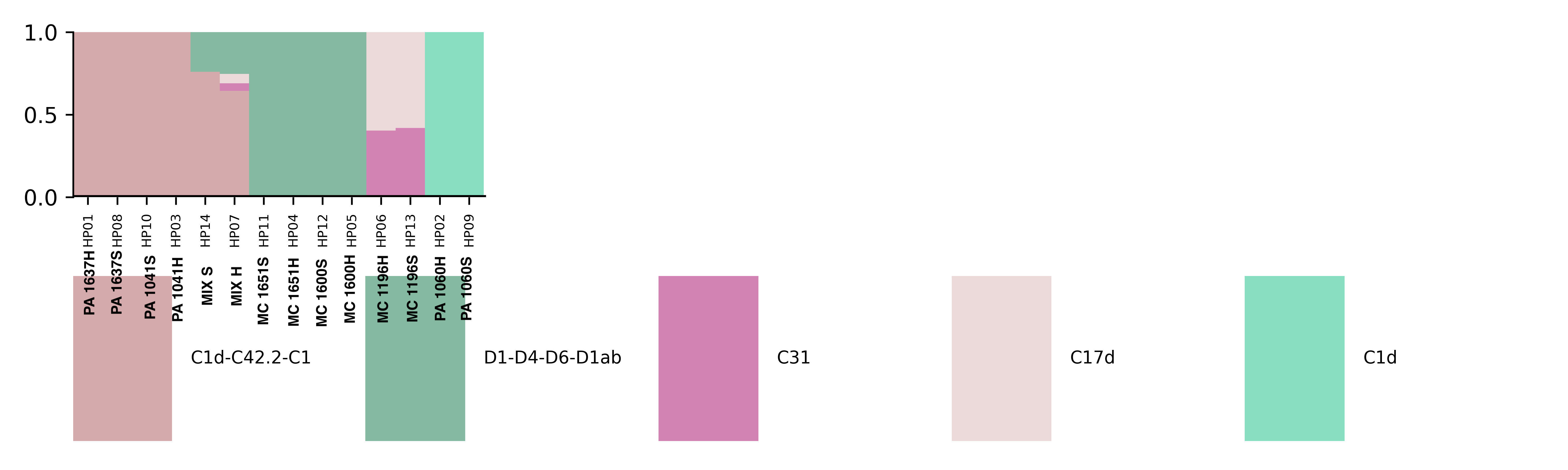
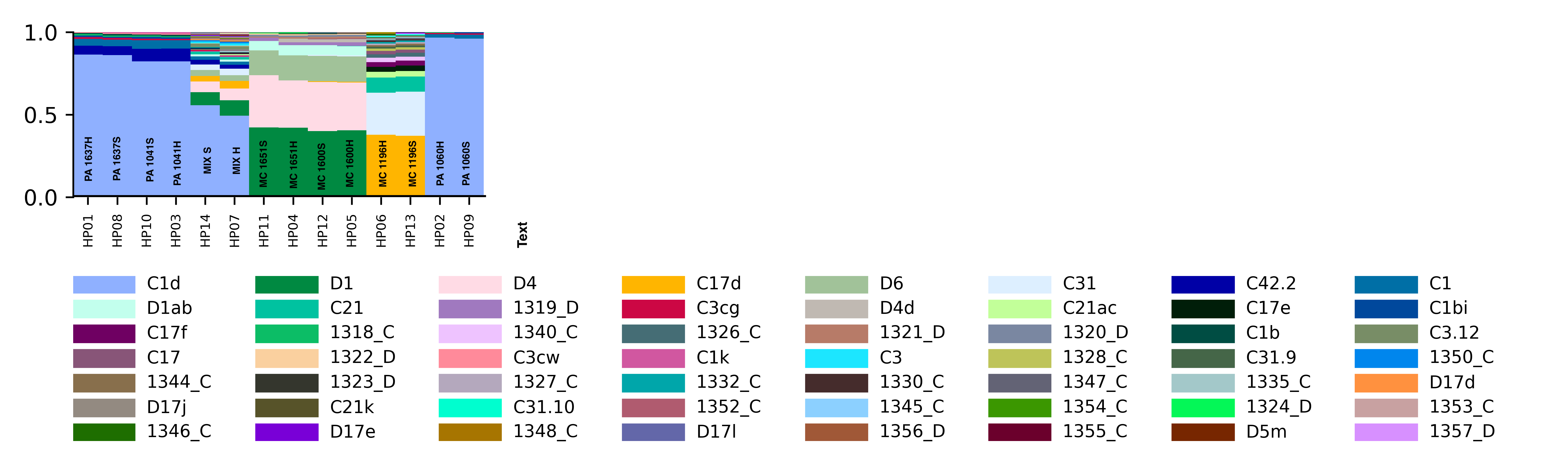
Major Take Home: Although this protocol is not effective, there is still a need to develop an efficient way to separate symbiont and host tissue for downstream genomic analysis. Ideas or suggestions? hputnam@uri.edu or emma_strand@uri.edu.
Protocol Preparation
Reagents and supplies
- RNAse Away
- RNA/DNA shield
- RNAse-free water
- Proteinase K digestion buffer
- Proteinase K
- Isopropanol
- 10mM Tris HCl pH 8.0 made with RNase-free water
- 10% bleach
- Zymo Duet DNA/RNA Extraction kit buffers: DNA/RNA lysis buffer, DNA/RNA Prep Buffer, DNA/RNA Wash Buffer, DNA Digestion buffer, and DNase I
Equipment
- Rocking oven that can be set at 55 °C
- Thermomixer
- Vortexer
- Qiagen Tissue Lyser: Handbook
- Bead tubes: 2mL 0.5mm glass beads and tubes from Fisher Scientific
- Designated RNAse free space
- Tabletop and larger centrifuges for 1.5 mL capable of 12,000xg
- Clippers
Reagent Preparation
- Add 96 mL 100% ethanol (104 mL 95% ethanol) to the 24 mL DNA/RNA Wash Buffer concentrate before use. DNA/RNA Wash Buffer included with D7003T (Mini Prep Plus Kit) is supplied ready-to-use and does not require the addition of ethanol prior to use. Check kit contents and instructions to confirm prep steps.
- Reconstitute the lyophilized (freeze-dried) DNase I as indicated on the vial prior to use. Mix by inversion. Store frozen aliquots.
- Reconstitute the lyophilized (freeze-dried) 20 mg Proteinase K with 1040 uL Proteinase K Storage Buffer or lyophilized (freeze-dried) 5 mg Proteinase K with 260 uL Proteinase K Storage Buffer. Vortex to dissolve. Store at -20 °C.
Fragment Preparation
Sterilizing working area: I. Rinse clippers with:
- 10% bleach solution
- DI water
- Isopropanol
- RNAse free water
II. Spray gloves with RNAse away and rub hands together.
Take fragments one at a time out of the freezer and sterilize clippers in between every fragment. These steps are time sensitive to prevent the coral fragments and freezer from thawing. Do not rush, but be efficient.
Assign “extraction numbers” to each ID for ease of labeling. See below chart for an example:
| Extraction # | Coral ID | Species | Homogenization |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1123 | Montipora | Soft |
| 2 | 1123 | Montipora | Hard |
| 3 | 1769 | Montipora | Soft |
| 4 | 1769 | Montipora | Hard |
| 5 | 1056 | Pocillopora | Soft |
| 6 | 1056 | Pocillopora | Hard |
| 7 | 1607 | Pocillopora | Soft |
| 8 | 1607 | Pocillopora | Hard |
Clipping fragment:
- Label the lid of a bead tube with the coral fragment’s sample ID number, and the side of the tube with the coral fragment ID and today’s date.
- Add 1000 μl of RNA/DNA shield to the bead tube.
- Remove desired fragment from -80 °C freezer.
- Using sterilized clippers, clip off 1-2 small pieces and place into the bead tube. RNA/DNA shield needs to cover the fragments.
Repeat above steps 1-5 for each fragment before moving on.
Soft and Hard Homogenization
- Vortex for Pocillopora fragments for 1 minute and the Montipora fragments for 2 minutes. Leave the settings on and on max power. This is the “soft homogenization” step.
- After vortex time, check to see if the tissue is coming off of the skeleton and look for coloration change in shield liquid.
- Remove supernatant from the bead tube and place in a new 1.5 microcentrifuge tube labeled on the side with the extraction ID number, coral fragment’s sample ID number, “soft”, and today’s date. Label the cap of the microcentrifuge tube with the extraction number. This supernatant will become the sample for “soft homogenization”. The remaining chunks of fragment will become the sample for “hard homogenization”.
- Add 500 μl of RNA/DNA shield to the bead tube with the coral fragment pieces. RNA/DNA shield needs to cover the fragment pieces.
- Place the beads tubes with the coral fragment pieces in the Qiagen Tissue Lyser Adapter Set 2 x 24.
- Operate the Tissue Lyser for 1 minute at 20 Hz.
- Remove the supernatant and put in a new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube labeled on the side with the extraction ID number, coral fragment’s sample ID number, “hard”, and today’s date. Label the cap of the microcentrifuge tube with the extraction ID number.
- Add 300 μl of sample, 30 μl of Proteinase K digestion buffer (10:1 ratio of sample:digestion buffer), and 15 μl of Proteinase K (2:1 ratio of digestion buffer:Proteinase K) to a new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube.
At this point, each coral fragment should have 2 tubes to move forward to extractions with: one for soft homogenization and one for hard homogenization.
For 4 coral fragments: 4 bead tubes with coral fragment pieces, 8 tubes with leftover homogenate sample (4 soft, 4 hard), and 8 tubes with homogenate, Proteinase K digestion buffer, and Proteinase K (4 soft, 4 hard). - Vortex and spin down all tubes.
- Place bead tubes and leftover homogenate tubes in -80 °C freezer.
Zymo Duet RNA DNA Extractions
Modified from the Zymo protocol.
DNA Extraction
- Set up yellow DNA spin columns and collection tubes, label appropriately
- Warm elution liquids to 70 °C (10mM Tris HCl pH. 8.0 and RNase free water)
- Add equal volume (to supernatant; 345 µl) DNA/RNA lysis buffer to each sample tube
- Finger flick to mix tubes
- Add 700 µl (total volume) of sample gently to the yellow DNA spin column
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Important Save the flow through from this step: transfer to a new 1.5mL tube labeled for RNA
- Add 400 µl DNA/RNA Prep Buffer gently to the yellow DNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 700 µl DNA/RNA Wash Buffer gently to the yellow DNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 400 µl DNA/RNA Wash Buffer genetly to the yellow DNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 2 minutes
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Transfer yellow columns to new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (“E1”)
- Add 10 µl warmed 10mM Tris HCl to each yellow DNA column by dripping slowly directly on the filter
- No incubation for the first elution. Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Transfer the yellow DNA columns to new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (“E2”)
- Add 100 µl warmed 10mM Tris HCl to each yellow DNA column by dripping slowly directly on the filter
- Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Aliquot 10 µl of the second elution (“E2”) to 0.5 mL PCR tubes for Qubit and Gel Electrophoresis analysis.
- Store at 4 °C if quantifying the same day or the next, if waiting longer store in -20 °C freezer
RNA Extraction Can do concurrently with DNA Extraction after DNA Extraction Step 7
- Add equal volume (700 µl) 100% EtOH to the 1.5 mL tubes labeled for RNA containing the original yellow column flow through
- Vortex and spin down to mix
- Add 700 µl of that liquid to the green RNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 700 µl to the green RNA spin columns (the rest from the 1.5mL RNA tubes)
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Get DNase I from freezer
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 400 µl DNA/RNA Wash Buffer gently to each green RNA column
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Make DNase I treatment master mix:
- 75µl DNA Digestion buffer x # of samples
- 5µl DNase I x # of samples
4 coral fragments (8 samples total): 600 µl of buffer and 40 µl of DNase I
8 coral fragments (16 samples total): 1,200 µl of buffer, 80 µl of DNase I
10 coral fragments (20 samples total): 1,500 µl of buffer, 100 µl of DNase I. Place in 5 mL tube instead of 1.5 mL tube.
- Add 80 µl DNase I treatment master mix directly to the filter of the green RNA columns
- Incubate at room temp for 15 minutes
- Add 400 µl DNA/RNA Prep Buffer gently to each column
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 700 µl DNA/RNA Wash Buffer gently to the green RNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Add 400 µl DNA/RNA Wash Buffer genetly to the green RNA spin columns
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 2 minutes
- Discard flow through (Zymo kit waste)
- Transfer green columns to new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes
- Add 50 µl warmed DNase/RNase free water to each green RNA column by dripping slowly directly on the filter
- Incubate at room temp for 5 minutes
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rcf (g) for 30 seconds
- Repeat steps 25-27 for a final elution volume of 100 µl
- Aliquot 5 µl of the final elution to 0.5 mL PCR tubes for Qubit and TapeStation analysis.
- Store all tubes in the -80 °C freezer.
Clean-up
- Place tissue and liquid in the waste container labeled Zymo extraction waste.
- Wipe down RNA free area with RNase away and kimwipes.
- Throw away all tips and restock tip boxes if necessary.
Testing Quantity and Quality
To test RNA and DNA quantity: Qubit
To test RNA quality: TapeStation
To test DNA quality: Gel Electrophoresis
Solution Key:
DNA/RNA Lysis Buffer: Contains a high concentration of chaotropic salts, which destabilize hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces and hydrophobic interactions. This destabilizes proteins, including nucleases. The buffer will also disrupt association of nucleic acids with water.
DNA/RNA Wash Buffer: Used to remove residual proteins and carbohydrates, and purifies the molecular end product.
DNase I: deoxyribonuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. This is used in the RNA extraction step to purify RNA final product.
DNA/RNA Prep Buffer: Ethanol and guanidinium chloride used a deproteinization measure. Guanidinium is a very strong denaturing agent that will dissolve cells and RNAses.
EtOH: the addition of alcohol further enhances and influences the binding of nucleic aicds to the silica (see spin colum description below).
10 mM Tris HCl: DNA is more stable at slightly basic pH and will dissolve faster in a buffer than water. Using Tris instead of water will enhance rehydration of high molecular weight DNA.
DNA/RNase free water: Used as an elution in the RNA extraction steps. RNA can tolerate a slightly acidic pH and dissolves. Warmed water as an elution increases high molecular yield.
Yellow DNA/Green RNA Spin Columns: contain a silica membrane that binds to nucleic acids. Proteins and polysaccharides should be in the flow-through liquid that is discarded while RNA and DNA is kept on the membrane.
Proteinase K: an enzyme that cleaves the peptide bond in proteins next to the carboxyl group of hydrophobic amino acid residues. This decontaminates the sample and leaves purified DNA/RNA.
General workflow of an extraction:
- Cell lysis through disruption of cellular membranes
- Dehydration and precipitation of the cellular proteins (protein denaturation)
- Separation of cellular proteins and other cellular components out of the nucleic acid
- Precipitation and dissolving the nucleic acid
Helpful links:
How DNA RNA extraction kits work
DNA Extraction and Purification
DNA Extraction Methods
Troubleshooting
More info coming soon.
Unix Shell Basics
Navigating Unix Shell
Zymo-Duet-RNA-DNA-Extraction-Protocol
Zymo Duet DNA/RNA Extraction Protocol
TapeStation Protocol
TapeStation Protocol
Qubit Protocol
Based on Putnam Lab Protocol written by M. Schedl: Qubit
Lab Plan for Holobiont Integration Project
Lab Plan for Holobiont Integration project
Acropora eggs/sperm DNA and RNA Extractions
E. Strand, E. Chille 20190528 DNA/RNA Extractions, Qubit
E. Strand 20190529 Tape Station
E. Strand, M. Schedl 20190529 Ship Samples
Acropora eggs/sperm DNA and RNA Extractions
E. Strand, E. Chille 20190528 DNA/RNA Extractions, Qubit
E. Strand 20190529 Tape Station
E. Strand, M. Schedl 20190529 Ship Samples
